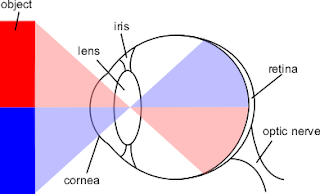
The are covered by the image on the retina can be enlarged by increasing the angle. Howeverer, the object can not be placed neither too close (near point, 25 cm in average) nor too far (far point, infinity) way.
Farsighted people have near point further away than 25 cm. This is because the the eye ball is too shor or the cornea is not curved enough. Nearsighted people have far sight closer than infinity. The reason can be too long eye ball or too curved cornea.
Take a look here how to fix farsightedness and nearsightedness.